"Informed AI News" is an AI-curated publications aggregation platform, ensuring you access only the most valuable information, with the aim of eliminating the information gap and transcending the confines of information cocoons. Find out more >>
Scientific Breakthrough in Imaging Radioactive Cesium from Fukushima Disaster
- summary
- score

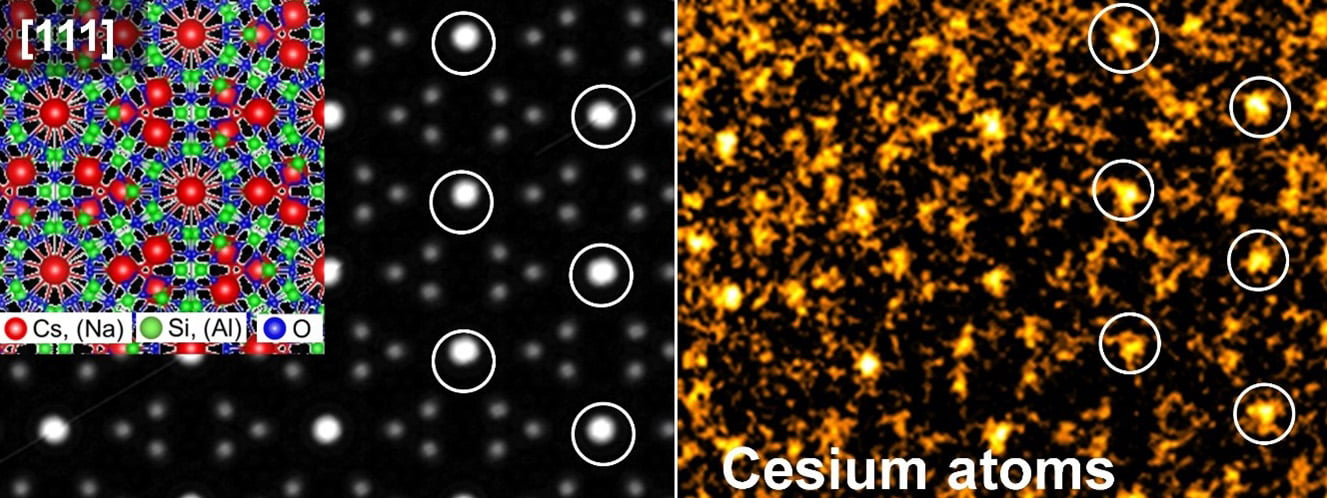

Summary: After 13 years since the Fukushima nuclear disaster, scientists have achieved a groundbreaking feat: direct imaging of radioactive cesium in environmental samples. Published in the Journal of Hazardous Materials, this international collaboration used advanced electron microscopy to visualize cesium atoms, previously unseen at the atomic level. This discovery not only sheds light on the distribution of cesium but also informs strategies for reactor decommissioning and waste management.
Key Insights: The imaging of radioactive cesium, a byproduct of nuclear fission, offers critical insights into the lingering environmental and health impacts of the Fukushima disaster. The cesium, found in microscopic glass-like particles, presents unique challenges for cleanup and safety. This research underscores the complexity of nuclear decontamination and the importance of international scientific collaboration in tackling such global hazards.
Explanation of Terms:
- Radioactive Cesium (Cs): A radioactive element produced by nuclear reactions, known for its environmental persistence and health risks due to its ability to contaminate food chains and cause cellular damage.
- High-Resolution High-Angle Annular Dark Field Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (HR-HAADF-STEM): A sophisticated microscopy technique that allows for the visualization of individual atoms within a sample, crucial for analyzing materials at the atomic scale.
- CsMPs (Cesium-Rich Microparticles): Tiny particles containing high levels of radioactive cesium, formed during nuclear meltdowns and dispersed into the environment.
- Reactor Decommissioning: The process of safely dismantling and disposing of a nuclear reactor after it has been permanently shut down, which involves complex and hazardous procedures due to radioactive contamination.
| Scores | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Objectivity | 6 | Content provides a balanced overview of the scientific achievement with factual support. |
| Social Impact | 4 | The research influences public understanding and policies related to nuclear safety and cleanup. |
| Credibility | 5 | The research is published in a reputable journal, supported by scientific methods. |
| Potential | 5 | The findings could significantly impact nuclear decommissioning and environmental safety strategies. |
| Practicality | 4 | The imaging technique has direct applications in nuclear safety and environmental monitoring. |
| Entertainment Value | 2 | While informative, the content lacks typical entertainment elements. |