"Informed AI News" is an AI-curated publications aggregation platform, ensuring you access only the most valuable information, with the aim of eliminating the information gap and transcending the confines of information cocoons. Find out more >>
Revising the Narrative of Human Origins in East Africa's Great Rift Valley
- summary
- score



Summary:
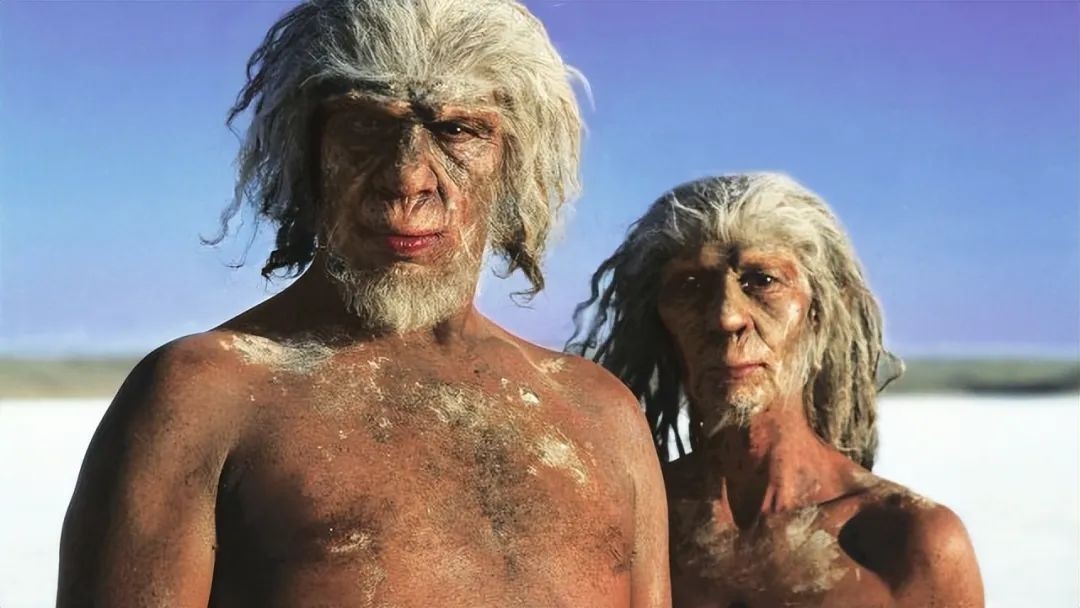
The narrative of human origin, centered around East Africa's Great Rift Valley, is being reevaluated. Traditional accounts suggest that modern humans, or Homo sapiens, evolved in this region about 150,000 years ago, with a pivotal cognitive leap occurring around 70,000 years ago. This leap is said to have equipped our ancestors with symbolic thinking, setting them apart from other species and enabling their global dispersal.
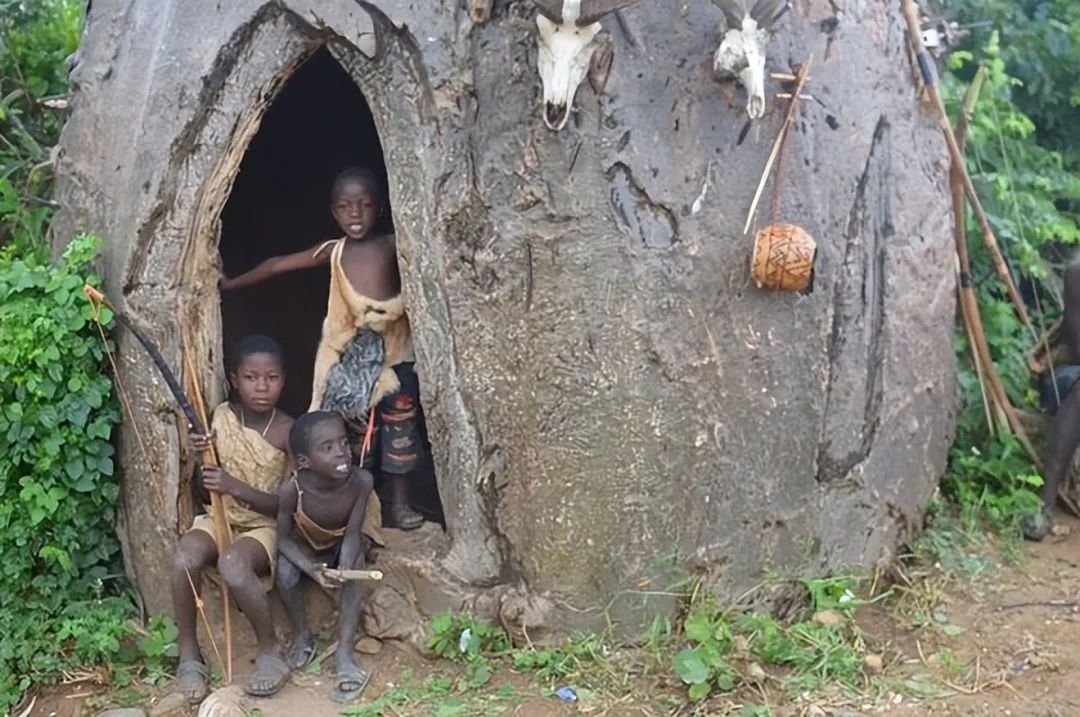
However, recent discoveries challenge this linear progression. Fossils and archaeological evidence from southern Africa indicate complex symbolic behavior dating back much further than 70,000 years. Genetic studies also reveal that certain indigenous groups in southern Africa, like the San people, have a lineage distinct from other human populations, dating back at least 350,000 years.
Moreover, the Congo Basin, largely overlooked due to its challenging environment, suggests an early human presence predating major agricultural expansions. Ancient DNA from this region links contemporary hunter-gatherers to much older ancestral populations.
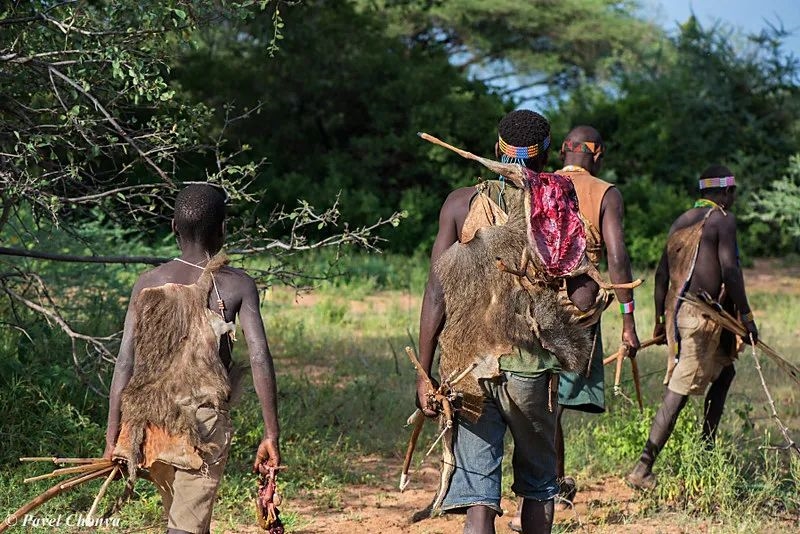
The concept of a pan-African social network further complicates the narrative. Evidence of long-distance trade in goods and ideas, such as beads and tools, suggests a mosaic evolution where isolated developments were periodically integrated across vast distances. This network implies a more dynamic and interconnected human evolution, rather than a simple, linear progression from one region.
Insights:
The reevaluation of human origins underscores the complexity of our evolutionary journey. It challenges the notion of a singular birthplace and a linear path of development. Instead, it suggests a rich tapestry of human adaptation and interaction across diverse environments. This mosaic evolution, characterized by periods of isolation and integration, likely fostered both genetic and cultural diversity, enhancing our species' resilience and adaptability.
Explanation of Terms:
- Homo sapiens: The scientific name for modern humans, distinguished by their cognitive abilities and physical characteristics.
- Cognitive leap: A significant advancement in mental capabilities, such as the ability to use symbols and abstract thinking.
- Mosaic evolution: An evolutionary pattern where different traits evolve at different rates or in different ways, rather than a uniform progression.
- Pan-African social network: A hypothesized ancient network of human interaction across Africa, involving the exchange of goods, ideas, and possibly genes.
| Scores | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Objectivity | 6 | Content provides a balanced view of the reevaluation of human origins, incorporating recent scientific findings and diverse perspectives. |
| Social Impact | 4 | Content sparks discussion on human evolution and challenges traditional views, influencing public opinion in anthropology and related fields. |
| Credibility | 5 | Content is based on credible scientific research and evidence, sourced from archaeological and genetic studies. |
| Potential | 5 | Content has high potential to influence future research and understanding of human evolution, potentially leading to significant changes in accepted theories. |
| Practicality | 4 | Content is practical for academic and scientific communities, providing new insights and directions for research in human evolution. |
| Entertainment Value | 3 | Content has some entertainment value for those interested in anthropology and human origins, though it may not appeal to a broad audience. |