"Informed AI News" is an publications aggregation platform, ensuring you only gain the most valuable information, to eliminate information asymmetry and break through the limits of information cocoons. Find out more >>
New Antibiotic Compound Shows Promise in Treating Severe Bacterial Infections
- summary
- score
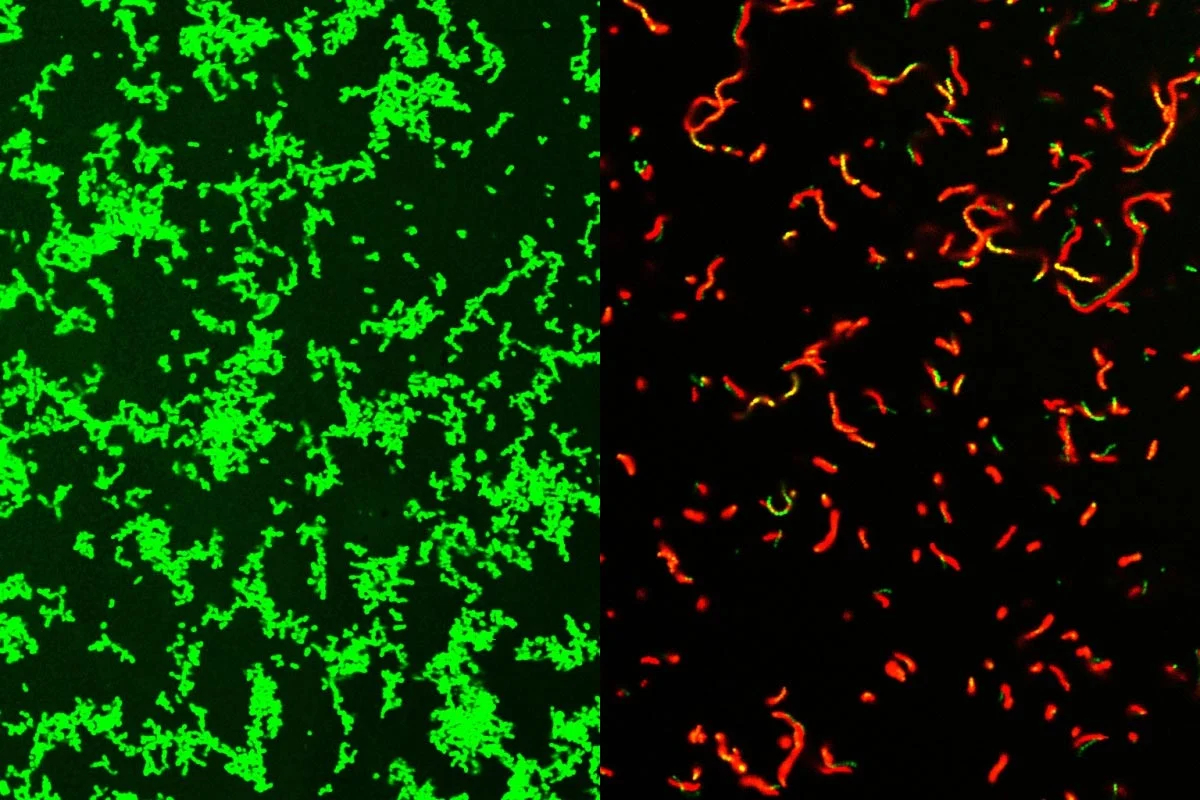
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have developed a new antibiotic compound, GmPcides, effective against severe bacterial infections in mice, including those that cause "flesh-eating" diseases. This compound targets Gram-positive bacteria, known for causing drug-resistant infections and toxic shock syndrome.
The compound, based on a molecule called cyclo-2-pyridone, was initially designed to prevent bacterial adhesion to urinary catheters. However, it unexpectedly showed broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. GmPcides work by disrupting bacterial cell membranes, making them permeable and impairing their functions.
Tests on mice with necrotizing soft tissue infections, including necrotizing fasciitis, showed significant improvements in healing and reduced bacterial virulence. Importantly, GmPcides appear resistant to the development of bacterial resistance.
The inventors have patented the compound and licensed it to QureTech Bio, aiming for clinical trials and eventual market release. This interdisciplinary approach, combining microbiology, chemistry, and medicine, highlights a promising strategy to combat multi-drug resistant bacteria.
| Scores | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Objectivity | 6 | Comprehensive reporting with in-depth analysis. |
| Social Impact | 5 | Significantly influences public opinion on antibiotic resistance. |
| Credibility | 5 | Solid evidence from authoritative sources. |
| Potential | 6 | Inevitably leads to significant changes in treatment methods. |
| Practicality | 5 | Widely applied in practice, achieving good results. |
| Entertainment Value | 2 | Includes a few entertaining elements. |