"Informed AI News" is an AI-curated publications aggregation platform, ensuring you access only the most valuable information, with the aim of eliminating the information gap and transcending the confines of information cocoons. Find out more >>
Ancient Zircon Crystals Suggest Early Presence of Fresh Water and Land on Earth
- summary
- score
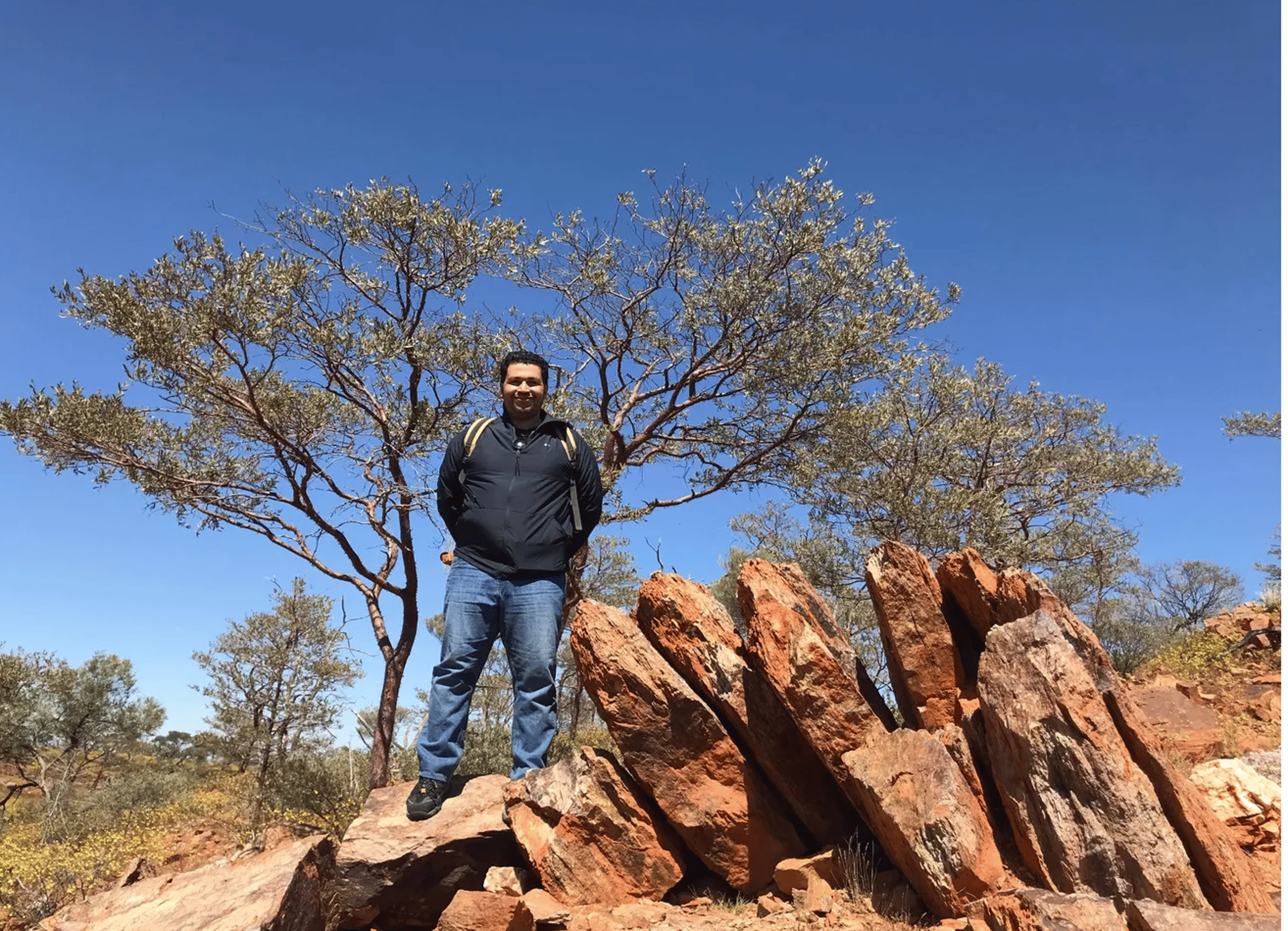
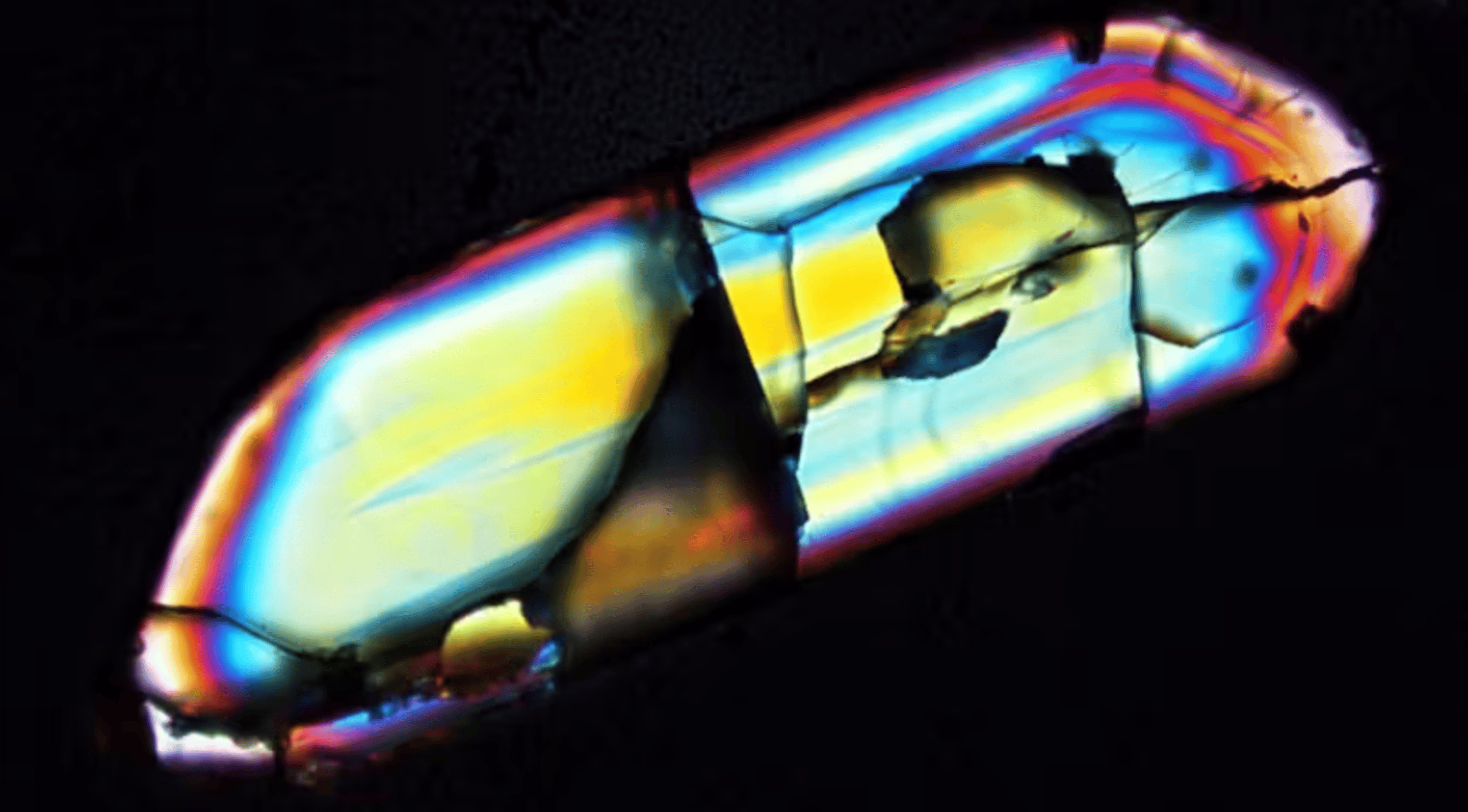

New research on ancient zircon crystals from Australia reveals that Earth had fresh water and dry land 4 billion years ago, 5 billion years earlier than previously thought. Scientists at Curtin University analyzed these zircon crystals from Jack Hills, Western Australia, which are the oldest known terrestrial minerals. Zircon, nicknamed the "Time Lord," is highly resistant to erosion and transformation, making it a reliable historical record.
The team dated about 1,000 zircon grains, finding that 10% were over 4 billion years old. By measuring the ratio of heavy to light oxygen isotopes within these crystals, they detected a unique light oxygen signature, indicating the presence of fresh water. This discovery suggests that the hydrological cycle, crucial for sustaining life, began at least 4 billion years ago.
This evidence challenges previous theories that Earth was entirely covered by oceans 3 to 4 billion years ago. The findings not only shed light on Earth's early history but also suggest that land and fresh water might have facilitated the rapid emergence of life within 6 billion years of Earth's formation.
| Scores | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Objectivity | 6 | Content provides comprehensive reporting and in-depth analysis of scientific findings. |
| Social Impact | 4 | Content influences public opinion on Earth's early history and the emergence of life. |
| Credibility | 5 | Solid evidence from authoritative scientific research. |
| Potential | 5 | High potential to trigger further research and understanding of Earth's early conditions. |
| Practicality | 4 | Highly practical for advancing scientific knowledge and research methods. |
| Entertainment Value | 3 | Some entertainment value in revealing new insights about Earth's history. |